

Primers are usually composed of RNA and DNA bases and the first two bases are always RNA. A primer is therefore needed, at which nucleotides can be added. However, DNA polymerase cannot begin the formation of this new chain on its own and can only add nucleotides to a pre-existing 3'-OH group.
DNA STANDS FOR RIBONUCLEIC ACID FREE
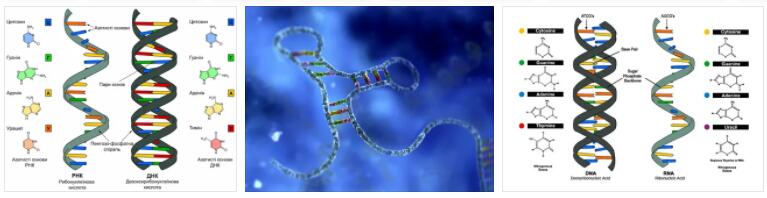
This opens up or “unzips” the double stranded DNA to give two single strands of DNA that can be used as templates for replication.ĭNA polymerase adds new free nucleotides to the 3’ end of the newly-forming strand, elongating it in a 5’ to 3’ direction. In this way, genetic information is transmitted from generation to generation.īefore replication can take place, an enzyme called helicase unwinds the DNA molecule from its tightly woven form. During this process, DNA polymerase “reads” the existing DNA strands to create two new strands that match the existing ones.Įvery time a cell divides, DNA polymerase is required to help duplicate the cell’s DNA, so that a copy of the original DNA molecule can be passed to each of the daughter cells. These enzymes are essential to DNA replication and usually work in pairs to create two identical DNA strands from one original DNA molecule. The DNA polymerases are enzymes that create DNA molecules by assembling nucleotides, the building blocks of DNA. The nitrogenous bases match up according the Chargaff’s Rules in which adenine (purine) always bonds to thymine (pyrimidine), and guanine (purine) always bonds with cytosine (pyrimidine).Purines are two ring nitrogenous bases and pyrimidines are single ring nitrogenous bases.Since these two strands are anti-parallel replication occurs in different directions on the DNA strand.The rungs of the ladder contain two nitrogenous bases (one from each strand) that are bonded together by hydrogen bonds.They also play an important role in the regulation of transcription.ĭNA is double stranded and shaped like a ladder, with the sides of the ladder made out of repeating phosphate and deoxyribose sugar molecules covalently bonded together. Each deoxyribose molecule has a phosphate covalently attached to a 3’ carbon and a 5’ carbon. The phosphate attached to the 5’ of one deoxyribose molecule is covalently attached to the 3’ of the next deoxyribose molecule forming a long single strand of DNA known as the DNA backbone. DNA strands run antiparallel to each other with one strand running in a 5’ to 3’ direction and the other strand running 3’ to 5’ when looking at the strands in the same direction. Nucleosomes are important for the safe storage of DNA. The nucleosomes arrange into coils, and in preparation for nuclear division, the coiled structure coils up again, to form a supercoiled chromosome. There is a short segment of naked DNA between each nucleosome.another type of histone, called H1, that binds the DNA to the central ‘bead’.two loops of DNA, approximately 150bp long, wrapped around 8 central histone proteins central histone proteins have structures that influence how tightly the DNA is packaged.A packaged unit of the chromatin fibre is called a nucleosome, which looks like a bead on a thread.For example, in each human cell there is approximately 2m of DNA distributed between 46 chromosomes, yet the average diameter of each cell is only 10–30µm. Each chromosome contains one very long DNA molecule.

DNA is arranged in chromosomes in eukaryotes.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
